Technical SEO: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners

Technical SEO is the general name of the on-site optimization efforts of a website to increase its performance in search engines. Technical SEO generally focuses on the technical elements that will enable a website to be more clearly understood and indexed by search engines. But it also includes elements that will increase user satisfaction. Technical SEO improves search engine rankings by working with other SEO studies, such as content quality and links.
How to Do Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is a comprehensive effort that requires you to improve your website in many different ways. Analyzing your website and your competitors beforehand can help you take a more accurate approach. However, following the headings below provides a good road map to eliminating the website’s deficiencies.
Page Titles and Meta Descriptions
Titles and descriptions are important for your SEO performance. Each of your pages should have a unique title and meta description. These disclosures are important for both browsers and users. To elaborate further:
Page Titles
It helps search engines understand the page’s subject. It must be descriptive and meaningful so that it can appear in search results. It may contain keywords, but it should be kept to 50-60 characters. Page titles exceeding 70 characters are not recommended, as they will not appear completely in the SERP.
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions following the page title summarize the page’s content to users. It is usually between 150-160 characters. Similarly, it may contain keywords, but the summary must be fluid and actionable to the user. Even though it is not important for search engine crawlers, every page must have a meta description. Meta descriptions can increase the rate at which users click on your page.
URL Optimization
Your website’s URL structures should be organized and updated. To optimize your URL for users and search engine crawlers, follow these steps.
SEO Friendly URL
You must consider the following points to have SEO-friendly URLs that search engines can understand.
Understandability: URLs need to be readable and logical. It should reflect the content in a short and meaningful way.
Categories: You can have more organized URLs by creating subfolders or directories.
Case and Characters: URLs are case-sensitive. Capital letters and the space between words take up more space and should be avoided.
For example, “https://roible.com/content-marketing-agency/” is a suitable URL.
Multilingual Websites
If your website is multilingual, you need to edit the URL configurations. With the “hreflang” HTML tag, search engines present content in the appropriate language to users. Make language and region tags to ensure that your content reaches your target audience.
To avoid language confusion on your website, you can make redirects similar to the example below:
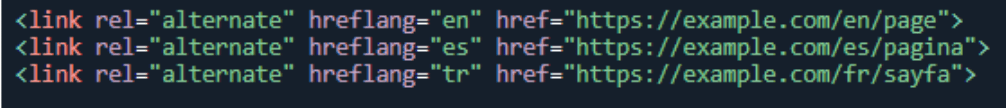
When using the hreflang tag, you must maintain duplexity. If you add a tag to each page with a language equivalent, the search engine will understand the relationship between the pages.
Canonical URL usage
You must use a canonical URL if you have similar content on your website. If crawlers detect identical content on your website, your page may be marked as duplicate content. To avoid this situation, you can show your status to browsers by using a canonical URL.
Navigation and Site Structure
An organized site structure and clear navigation can improve your website. Site structure is important for both search engine crawlers and your customers. Dividing your content into meaningful and simple categories will make it easier for users to find what they are looking for. An understandable navigation design will also improve user experience.
XML Sitemap
Creating an XML sitemap is an important step for search engine crawlers to understand your site. Crawlers consider the sitemap when crawling the site. Therefore, it is recommended that you add links, categories, and pages, paying attention to the hierarchy.
You also need to create a dynamic XML map for long-term SEO work. Your URLs or redirects may change over time. Therefore, you will not need to update with a dynamic map manually. Another issue you should pay attention to when creating a site map is the number of pages. A single sitemap cannot contain more than 50 thousand URLs.
You can learn about sitemaps, including XML, by reading Google’s sitemap guide.
Breadcrumb Menus and Pagination
Breadcrumbs are page path markers. It is especially recommended for e-commerce websites to use in terms of browsers and visitors’ experience. Breadcrumb menus are recommended because they facilitate hierarchy and navigation between pages. There is an example of a breadcrumb menu in the image below:
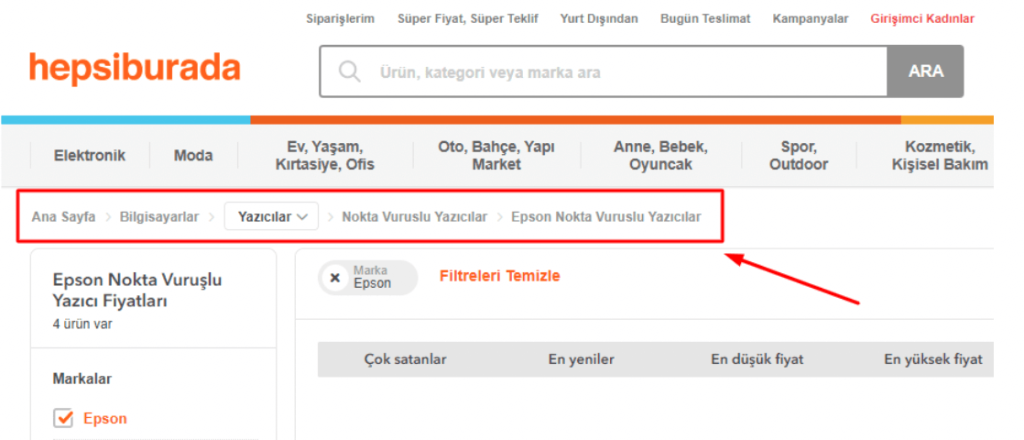
Users can easily access upper categories using the breadcrumb menu.
Pagination, translated as pagination, also serves the same purpose. As its name indicates, it is the separation of web content into pages. Similarly, numbered pages are often used on e-commerce sites.
Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Structured, organized data allows search engines to make sense of search queries. Structured data markup helps search engines understand your website better. By marking structured data, you can increase your website’s visibility to your target audience.
Structured data is usually added in Schema Markup or JSON-LD format. For example, a restaurant can use structured data to find the restaurant name, location, and opening hours and may specify information. This data helps users by providing more information in their search queries. Listed below are examples of structured data types:
- Embedded non-text objects: AudioObject, ImageObject, VideoObject
- Event
- Health and medical types: notes on the health and medical types under MedicalEntity.
- Organization
- Person
- Place, LocalBusiness, Restaurant …
- Product, Offer, AggregateOffer
- Review, AggregateRating
- Action
Server Optimization
Server optimization involves efforts to improve the performance of the server running your website. These optimizations range from speed to reliability.
HTTPS and Security
HTTPS stands for “Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure.” This protocol secures data transmission between websites, which is important for data security and users.
Current browsers may display warnings on websites that do not use HTTPS so that users may leave your website. Users who share personal or financial information can also choose to have their data encrypted.
SSL Certificates
It is recommended that you obtain an SSL, or “Secure Sockets Layer,” certificate instead of HTTPS. SSL will improve user experience and give you priority in search engines. Purchasing an SSL certificate and enjoying these benefits is easy. After purchase, you need to activate the SSL certificate on your server. Then, when you update your connections, you will have an SSL-certified website.
Website Speed and Media Optimization
You can apply the following methods to speed up your website and improve user experience.
- Web Caching: By storing frequently used data on the server, page loading speed is increased.
- Using CDN: With CDN, which stands for Content Distribution Network, you can store your content on different servers. This way, users experience faster performance by accessing the server closest to them.
- Gzip Compression: The web server compresses files so they download faster.
- Minification: Removes unnecessary spaces and characters to reduce the size of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
- Lazy Loading: It increases the overall page loading speed by delaying the loading time of media other than the content that appears when the page loads.
- Image Optimization: You can compress high-resolution images with lossy or lossless compression according to your quality and size demands. You should also choose the right format for your pictures.
- Video Compression: You can convert and compress videos to faster loading formats.
Rendering Systems
Search engine crawlers use one of two rendering systems when crawling websites’ JavaScript code: SSR or CSR.
Server Side Rendering (SSR)
Server Side Rendering, abbreviated as SSR, is a popular rendering method. In this method, the user’s request to view a page is transmitted to the server and answered by the server. The web page’s content is created by the server and sent to the browser. The browser’s job is less; it shows the website sent to it. SSR is generally more successful in terms of SEO and loading speed.
Client Side Rendering (CSR)
Client-side rendering (CSR) is a newer method. In CSR, the browser is responsible for loading JavaScript. The server sends the necessary files to the browser, which creates and displays the HTML file on the user’s screen.
Although the initial load speed is slower with CSR, it is still preferable as it reduces the load on the server. Additionally, on dynamic pages, content can be displayed without the need to repeat the entire page, improving the user experience.
Mobile Compatibility
Mobile-compatible websites may have higher rankings. Therefore, they should be designed to be responsive and support different screen sizes. Many search engines also focus on website performance on mobile.
You can measure your website’s success in terms of mobile compatibility with just one click. Tools like Google Search Console will help you with mobile-friendliness testing.
CSS/JavaScript
Responsive design in CSS and JavaScript codes is essential for mobile compatibility. Features such as media queries, flexboxes, and grid layouts will ensure that your content appears compatible with different screen sizes.
Additionally, simplifying navigation will increase mobile users’ satisfaction. By simplifying menus and keeping text readable, you can create a mobile-friendly website.
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)
AMP, or Accelerated Mobile Pages, is a method for providing a better mobile experience. It increases the speed of mobile pages with features such as caching, minimized CSS, and limited Javascript. It also includes special HTML tags for AMP optimization and a mobile-friendly URL configuration.
You can click on this link to access Google’s guide on AMP.
PWA (Progressive Web Apps)
PWA are web applications developed with modern web technologies that can work as applications on both browsers and mobile devices. PWA technology is advantageous as it requires much less time and budget than developing a mobile application. PWAs offer benefits such as offline access, higher performance than traditional websites, and better user experience. The only limitation is that users must use an up-to-date browser.
Core Web Vitals (CWV)
Web Vitals is the measurement standard that evaluates website performance developed by Google. CWV refers to the three main metrics within Web Vitals, these three metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) Measures the loading speed of the main content on the page. Ideally, this includes media elements such as video and should be less than 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): FID measures the response time to a user’s interaction. Ideally, users should receive a response within 100 milliseconds or less of their first interaction.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): CLS measures the layout change during a page’s loading process. Because different elements have different loading times, pages may experience unexpected position changes. CLS evaluates whether there is an element on the page that would cause the user to make an incorrect request, and ideally, a value below 0.1 is expected.
You can use Search Console to measure and evaluate your Web Vitals scores.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file tells the search engine which parts of your site it can and cannot crawl. You must guide the crawlers by specifying the pages you want or do not want to be crawled in the robot.txt file.
Indexing is a vital step for visibility, so it’s important that your robot.txt file accurately reflects your site. This file should contain pages that are prioritized for crawling. Different commands can be used in the robot.txt file. But most fundamentally, the pages that are wanted to be scanned and indexed are determined with the “allow” command. With the “Disallow” command, the crawling and adding of the page is prevented.
Not every page on your website may be useful to users, and you can hide these pages with robot.txt to improve the user experience. You can use Google’s source to get more detailed information about robots.txt.
Internal Links
You can establish intra-site links between pages on the website. Internal links are important for search engines to understand the hierarchy of pages. It also keeps users on your website longer. You can increase user satisfaction by answering visitors’ possible questions with in-site links.
HTTP Status Codes and URL Redirects
HTTP status codes are warnings and notes from the server. Recognizing the different status codes will come in handy in case of technical glitches.
100s and 200s
Status codes 100 and 200 are informative and indicate success. 100s indicate that the browser request has been received and is in progress. 200s indicate that this request has been successfully understood and accepted.
300’s URL Redirects
300s are defined as referral codes. This indicates that redirection is required because a new source is now being used for the requested content. For example,
- 301: Indicates that the web page has been permanently redirected.
- 302: Indicates that the web page has been temporarily redirected.
400s
400s are status codes that indicate there is a problem with the request. There are 400 status codes corresponding to different problems:
- 400: Indicates that the server could not process a request due to the browser.
- 403: Indicates that the user cannot access the content or is prohibited.
- 404: Indicates that the web page is not found on the server.
- 410: Indicates that the requested web page is definitely and permanently unavailable on the server.
500s
500s occur when a request the server can normally fulfill cannot be fulfilled due to an error. Depending on the error, different 500 status codes may be encountered:
- 500: Indicates that the request could not be fulfilled due to the server.
- 502: Indicates a problem occurred because the server received a negative response from a different server.
- 503: Indicates that the server is busy or in maintenance.
- 504: It usually indicates a technical problem caused by the server.
- 509: Indicates that the server has reached its monthly hosting traffic limit.
Domain Name Preference
The domain name no longer carries the same importance as it did a few years ago. Although shorter domain names were preferred in the past, length is not a big factor today. However, having a catchy and unique name can make it easier for your customers to find or remember you.
Similarly, domain extensions are more important for the user than local SEO. .com, .net, and .org, which are generally the more commonly used extensions. However, they do not affect SEO other than reflecting your credibility to users. However, if you are a company that does international SEO work, we recommend paying attention to domain extensions that depend on location. For example, .tr is a domain name extension affiliated with Turkey. Having your target audience and domain name extension parallel is an inevitable trick in international SEO.